How to use an external database with the FMR Docker image
The standard FMR Docker image is self contained in that includes everything needed to run a light-weight installation suitable for testing, personal use and light production workloads. But what happens if you want to use a database service external to the container? - SQL Server or Oracle for instance. This article explains how.
About FMR’s operating database
Just as a bit of background, FMR uses a SQL database for its operational storage - that is:
- structural metadata content
- settings and configuration information
- audits and transaction history
MySQL (5.7 and 8) is mature and free making it a good choice for many use cases. But FMR also supports Oracle (12c and 19c), Microsoft SQL Server and MariaDB.
During FMR installation, the database service and schema are defined either as a direct (JDBC) connection, or from FMR 11 by choosing a JNDI data source that must be pre-configured in the Java web application server.
When using the FMR Docker image, the installation phase has already been completed and the operating database set to the MySQL service internal to the container. However, that can be changed as explained in the following section.
Changing the FMR Docker database
Save existing structural metadata content
If you already have structural metadata in the container’s MySQL database, save it by exporting to file so that it can be reloaded when the new database is connected.
Log in as the root user:
- From
Export Structuresin the menu bar, choose All Structures. A Download Structures popup should appear. - Choose
FUSION-JSONfrom the list of formats, and check all of the boxes (Compress returned data etc) - Choose
Downloadto download all of the structures to a ZIP file which needs to be saved for later use.
Create a new schema on the external database service
FMR creates its own tables, but needs an empty schema (or ‘database’ depending on the terminology your database product uses). Create that and also a user account with privileges sufficient to create, modify and drop tables, insert, update and delete data. It’s this account that FMR will use to access the schema.
Change FMR’s database settings
Back in your running FMR Docker container…
Log in as the root user:
- Choose
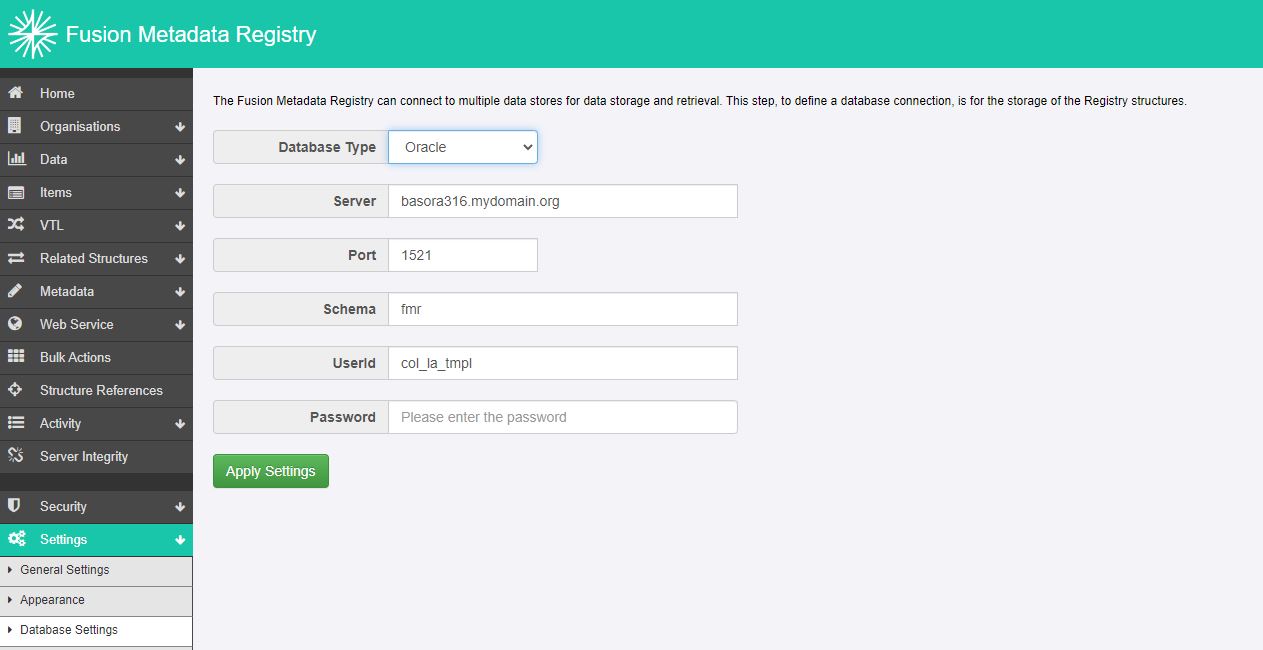
Settings>Database settingsfrom the menu bar. The current database settings reference the interal MySQL service so have:
Database Type = MySQL
Server = Localhost
Port = 3306
Schema = fmr
UserId = fmr_user
- Choose the type of the external database service.
For complex environments such as Oracle configured for HA-failover, chooseCustomwhich allows a custom connection string to be set. For most other use cases, the standardMySQL,OracleorSQL Serverconfigurations should be sufficient. ChooseMySQLfor MariaDB. TheJNDIoption requires manual modifications to the Docker container’s Apache Tomcat configuration and for that reason it’s not recommended unless you have a specific use case. - Set the database server hostname and port. The Docker container should inherit the DNS configuration from the host platform allowing a hostname to be used. If there are connection problems, try substituing the IP address instead.
- Set the schema, user ID and user password.
- Apply settings.
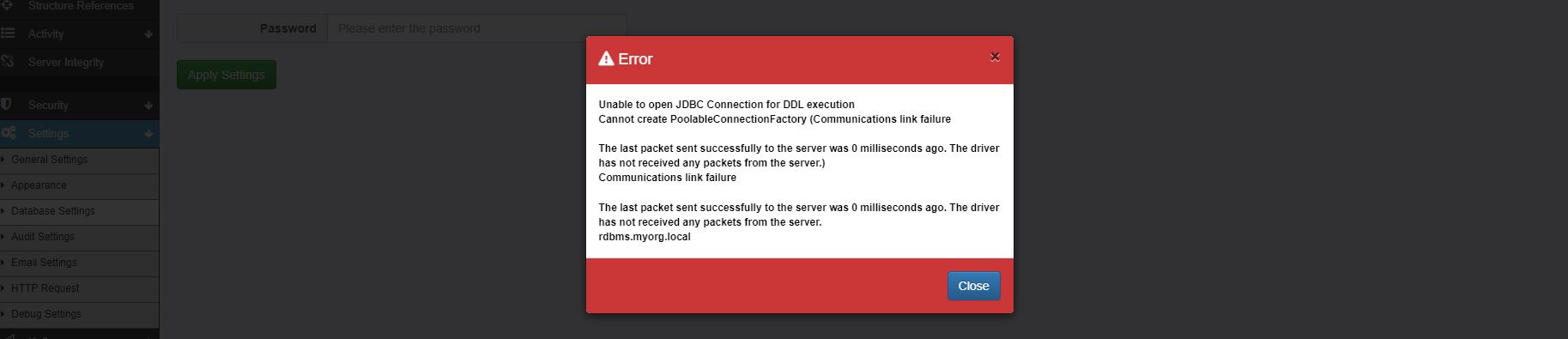
Check the new database connection is working
A ‘Database Updated’ message means a connection has been made successfully and FMR will reload its working environment from that database.
The most common source of failure is problems communicating with the external database service. The error report explains more:
Recreate settings, and reload any saved structural metadata
Settings such as Active Directory configuration and appearance aren’t exported with the structural metadata so will need to be recreated manually.
If structural metadata was exported in the first step, that can now be reloaded.
Log in as the root user:
- Choose
Load Structuresfrom the FMR home page. - Choose the File option and locate the file saved in the first step.
- For the Action choose
Replaceand clickImport Content.
Summary
The MySQL database service integrated with the standard FMR Docker image is convenient and suitable for many purposes, but some use cases demand a service external to the container is used. That’s possible by simply changing the the database connection details through the web user interface.